Vulnerability management
Concept
The Anyva Vulnerability management is an integral part of the comprehensive data protection and security concept in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It supports you in fulfilling your obligation to implement suitable technical and organisational measures, as described in particular in Art. 24, 25, 32 and 35 GDPR are required.
According to Art. 24 GDPR it is the responsibility of the controller to ensure compliance with data protection requirements through effective internal processes. Vulnerability management contributes to this, by systematically identifying, evaluating and documenting weaknesses in IT systems, processes and protective measures. This enables verifiable and continuous risk monitoring.
In line with Art. 25 GDPR ("Data protection through technology design and through data protection-friendly default settings") enables Anyva to Preventive detection and treatment of weak points already during conception, planning and implementation data processing processes and systems.
Art. 32 GDPR requires the security of processing to be guaranteed, particularly with regard to confidentiality, integrity and availability. Anyva fulfils this requirement through a Multi-level vulnerability management that takes into account both technical attack vectors (e.g. through CVEs) and organisational deficits (e.g. lack of access controls or unclear responsibilities).
Within the framework of Art. 35 GDPR (data protection impact assessment) is where Anyva shows its particular strength: Untreated vulnerabilities that affect relevant data protection requirements are automatically included in the assessment of the residual risk of a processing activity. This creates a dynamic risk picture that realistically depicts current threats - without additional documentation effort.
Anyva uses an intelligent combination of Asset linking, automated CVE check, comprehensible requirements modules and action tracking with effectiveness check. This architecture enables those responsible to implement data protection and information security not only in compliance with the law, but also efficiently and scalably - from small organisations to large corporations.
Realisation
Weak points are Known or potential security vulnerabilities in technical systems, organisational procedures or behaviour-related processes, that may compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of personal or other sensitive data.
In Anyva, vulnerabilities are categorised into:
| Type | Description of the |
|---|---|
| Technical weaknesses | Errors or configurations in hardware and software components, e.g. outdated software versions, open ports, unpatched security vulnerabilities (e.g. CVEs). |
| Organisational weaknesses | Missing or inadequate guidelines, processes or controls, e.g. lack of access concepts, unclear responsibilities or no training. |
| Process-related weaknesses | Gaps in processes or working methods, e.g. no logging of data transfer, media disruptions or missing approval processes. |
| Physical vulnerabilities | Risks due to spatial or infrastructural conditions, e.g. unsecured server rooms, inadequate fire protection or lack of access controls. |
| Behavioural weaknesses | Susceptibility to errors due to human behaviour, e.g. social engineering, careless handling of passwords or unrecognised phishing attempts. |
A vulnerability becomes relevant in Anyva when:
they have a defined Protection goal (confidentiality, integrity, availability, transparency, intervenability, non-linkability, etc.) are jeopardised,
No or inadequate safeguarding measures exist,
and/or relevant assets, processes or processing activities are affected.
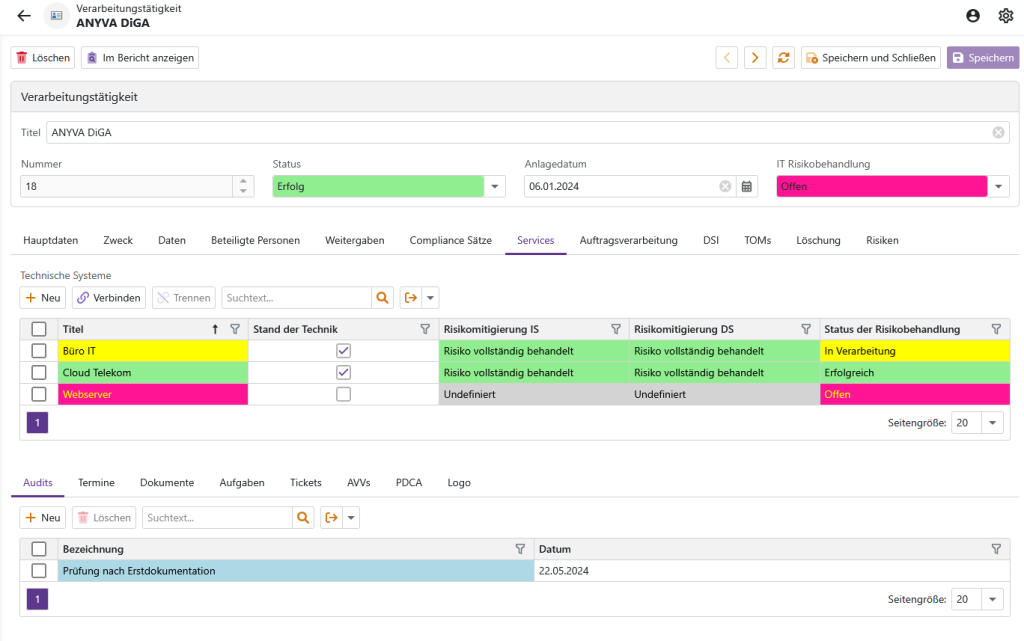
While organisational, procedural, physical and behavioural vulnerabilities can be identified and dealt with (mitigated) as part of the risk assessment by checking the requirements modules and regular review processes (PDCA), technical vulnerabilities have a dynamic, real-time character. It is therefore essential to identify newly identified weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the technical systems used as quickly as possible, preferably immediately, and to organise processes to prioritise them depending on their criticality.
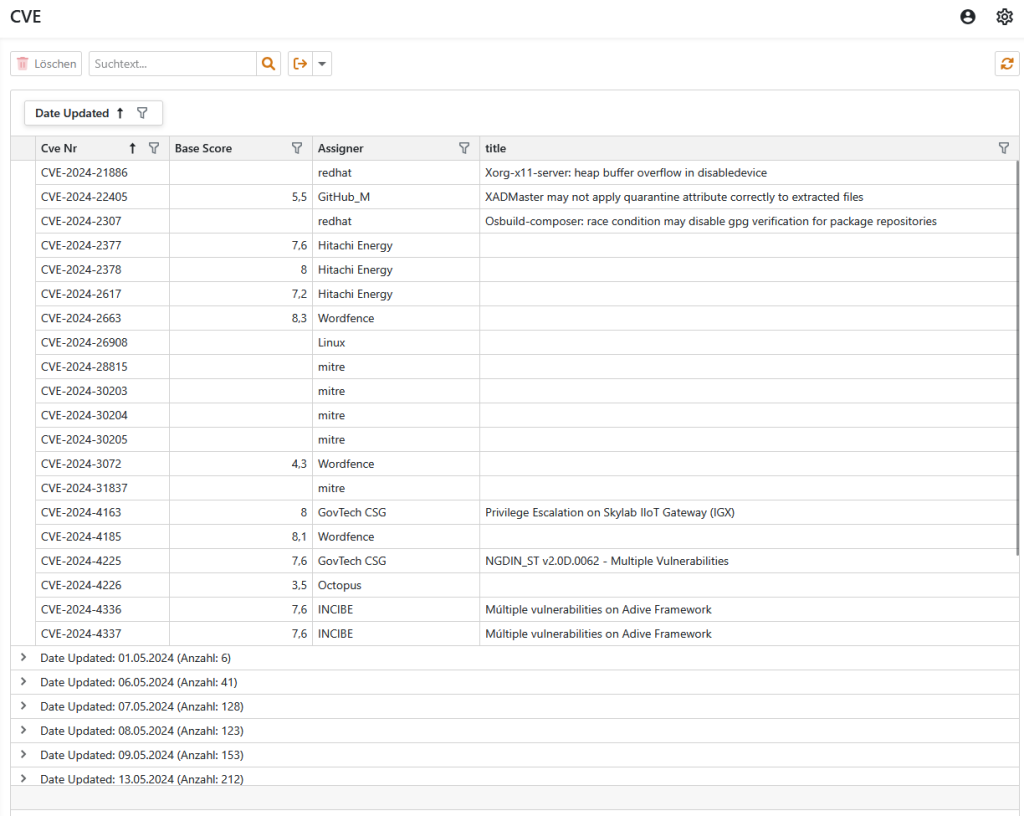
Anyva checks the MITRE CVE database checks for new entries every hour, downloads them to the local database and checks the entries for relevance in relation to the assets in the local asset database.
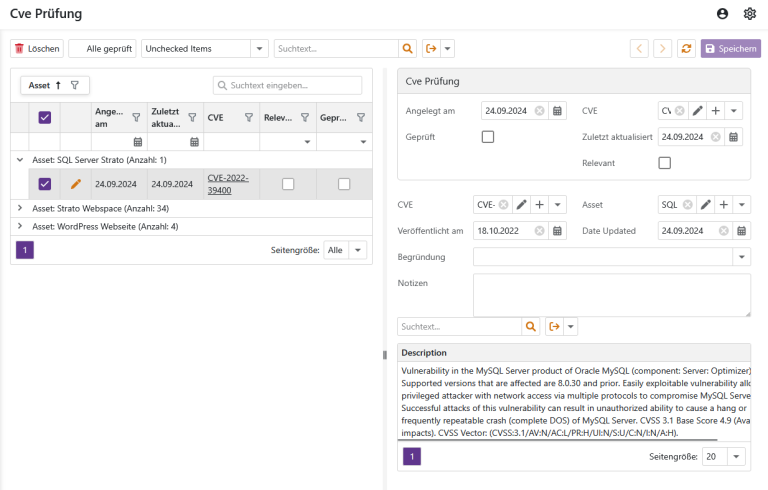
If Anyva recognises that a CVE entry could be relevant for a deployed asset, a check is initiated. Each asset contains a "notification list" with people who will be informed in such a case. Anyva uses AI functions to reduce the number of FALSE POSITIVES.
If a vulnerability found is automatically or manually recognised as "relevant", it is automatically assigned to the respective asset and marked as "open". The person responsible for the asset is notified by email.
As all processing activities and data protection impact assessments "know" which assets are used in their own context, they now also immediately receive information that the state of the art may no longer be complied with. The procedures "inherit" the risk status of the asset used that has the highest risk.